I’ve always assumed Renoir and Degas had similar issues with us fly tiers; a couple of decades spent on rigorous painting tedium, and saddled with the costs of painting supplies, groceries, and a roof overhead, true masterpieces were sacrificed for the more mundane portraiture … because painting Madame … paid the bills.
Fly fishing, especially during those cold months between Winter fisheries and Spring, endures a similar tedium, where inspiration comes occasionally, and inclement weather and work combine into books read, magazines thumbed through, and daydreams of future successes.
I used to find inspiration from periodicals, where fresh ideas and the exploration of new fisheries caused me a fit of tying creativity or made me lust after new terminal gear. Unfortunately, fresh ideas are in limited supply, and periodicals eventually yield to the stale yet profitable, and every Bahamian bone fishing article looks like ISIS reconnoitering Mosul, the difference between the two the color of their sun buff …
With the Internet and its ready access to all of the great colleges, organizations, and sources of fisheries research, the Scientific community is an underutilized source of freshness in angling ideas. Theories abound on fish, bugs, stream dynamics, global warming, and invasive species, and even a casual knowledge of fish and bug behavior allows the reader to follow along from proposal to conclusion.
The volume of research is staggering, and while much is in its infancy (and is best served as simple topics to mull), a great deal more is mature – and for anglers seeking new insight into their quarry or craft, become a source of ideas and topics that will never be mainstream enough to grace our angling press, or may feature conclusions that counter current ecological practices and are ignored by our conservation organizations.
In short, if you don’t turn over the stone yourself, no one will turn it for you.
This Spring has seen me start down a thread I found interesting, and resulted in many hours of fervor at the vise. What started simply – as a dissertation on Guppies has led through a chain of other papers, physics, and conventional wisdom, and while both conclusions and flies will always be questionable – the enjoyment of discovery and new inspirations have made the journey completely worthwhile.
The April issue of the Royal Society Proceedings B, has an article discussing the notion that patterns, motion, and coloration of prey (flora and fauna) are inheritable in Guppies, a freshwater fish.
After a great deal of rigorous experimentation the authors concluded Guppies prefer red or orange, and don’t particularly care much for blue. What fascinated me was the discussion that like bees, guppies were capable of honing in on patterns exhibited by their prey (both motion and coloration) akin to bees and birds and the specialized pollination coding on flowers.
For those as are unfamiliar, flowers are colored (both primary color and patterns of color on their petals) to attract the unique insects and birds that can best pollinate them. So long necked flowers that bees cannot climb into are coded for Hummingbirds, and anything with a long, thin proboscis that it can wad into the barrel of the flower.
This notion that freshwater fish may have similar tendencies I found fascinating, given that if anglers accept this notion it would likely spawn a bazillion new patterns that resembled (in coloration and pattern) everything from Green Drakes to discarded French fries.
As Mother Nature colors her insects to resemble the stream bottom, the notion of red or blue is a bit far fetched, but it does buttress our notion that color of the natural is worth imitating, in either dry or wet variants. Inheritance would also ensure that planted fish, should they survive, would also trend toward the same food choices of wild fish – as both groups must dine off the same menu.
Color and shape are the most copied trait of the modern fly tier, a reflection of the prevailing “match the hatch” logic that has dominated fly fishing for the last several decades. Patterns in coloration and motion are the “less traveled” path, given how fly tying materials have dictated how the resultant imitation moves.
Natural materials being a bit more lively than synthetics, but only by accident, as many natural materials can be stiffened by the simple act of attachment to the hook.
Having to use a “J-shaped” bit of steel to contain all the parts of the natural is also a delimiting factor. Any discussion of imitation has to also recognize the limitations of physics on our potential options.
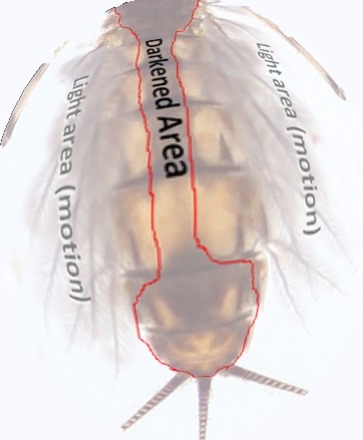
After a couple of weeks ferreting out full motion videos of mayfly nymphs in their natural settings, and viewing them for signatures akin to how a bee might view flowers, it is quickly apparent that there is a couple of patterns of color on a typical mayfly when swimming. The first was due to its carapace and color density imbued by thickness, and the second was due to gill motion, and the lightening effect that lateral gills (and the light-colored cilia attached) and their constant motion have on the surrounding colors of the insect.
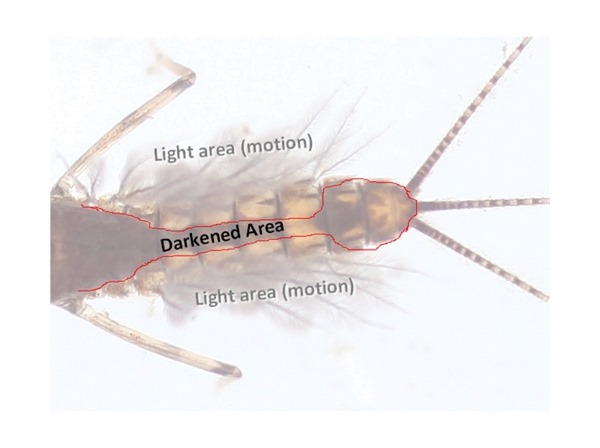
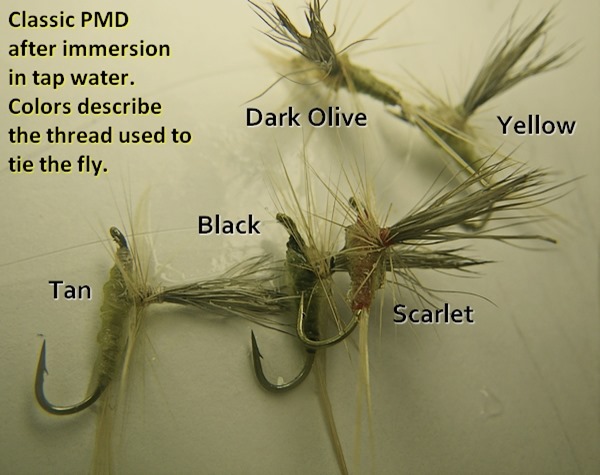
Should this wild notion of torso “pattern-key” being the missing ingredient in the complete subjugation of Salmonids, I could expect some lofty company. The thought of my Portly & Brazen suddenly synonymous with Gordon, Skues, or Sawyer was pretty heady, but a couple of decades of wisdom tempered my flirtation with ego.
Tying flies with this type of pattern in their torso had some very obvious shortcomings …Physics being the most sinister, as all of my full motion vignettes quickly displayed.
 In moving water most fish face upstream. Insects dislodged due to mishap or swimming to the surface come downstream (roughly) head first. Fish on the prowl for targets likely don’t see anything of the abdomen patterning save the wink of dark top or light belly, and only if the insect is swimming in its customary violent tail-centric, up-down, fashion.
In moving water most fish face upstream. Insects dislodged due to mishap or swimming to the surface come downstream (roughly) head first. Fish on the prowl for targets likely don’t see anything of the abdomen patterning save the wink of dark top or light belly, and only if the insect is swimming in its customary violent tail-centric, up-down, fashion.
In still water the fish can encounter an underwater insect along any axis, and the predative view may not even involve any signature other than motion, the frantic attempt to evade being eaten triggering the pursuit.
Not to mention the notion of the fish’s eye not being the same as our stereo flavor, and the exaggerations of coloration that exist when converting a stereo image to an approximation of what we think fish see …
… and therein lies the beauty of Science and the unending appeal it has for me and my dull Winter months. A constant stream of facts and theorems that promise future success – all of which must be tempered with angling wisdom and experience, in order to determine which theory will fill next season’s fly box.
What’s not important is whether any chain of facts will result in more fish caught, as the angler cannot determine what he would have done had he fished other flies. What is worthy is to continually question the status quo, given the shaky ground all of our current angling truisms are built upon.


