It’s the fish you think of on slow days and rekindles flagging interest. It’s the fish that makes up for fussy trout and flies smaller than #20, it’s salve for a season of sunburn and mosquito bites, cures hangovers, and for a couple of too-short months allows us to focus on important fishing principles like spite and revenge.
It’s Alosa sapidissima, the American Shad – and while you may have fished for them hundreds of times, I guarantee you know less about their habits, food preferences, and history – than any of the other gamefish you chase regular.
Why? Simple, it’s a glutton for bright and shiny, shows little selectivity and is available in enormous numbers – so you’ve never had to wrinkle a brow or crack a book to be successful.
I’m the first to admit guilt, having asked the questions of those more experienced – and assumed they spoke gospel. Now with millions of the Silver Horde ascending my rivers, and with the next couple of months devoted to their complete and utter exploitation, I’ve no excuse not to learn more …
“Know thy enemy and know thy self and you will win a hundred battles.”
Much of the research on American Shad are from their native Eastern drainages, and it’s a story that doesn’t match well with what’s been relayed in idle banter on the river bank.
East Coast Shad are distributed as far south as North Carolina, yet multiple genetic strains are responsible. They are an anadromous fish, but in their southern range and warmer water – are like our Pacific salmon, spawning once before dying.
Colder water allows the fish to make the multiple migrations like the steelhead trout, with an average lifespan of about a decade. How long they can survive in the river is dependant on the sex and size of the fish when it enters fresh water, and measuring your local fish can assist in determining how long they’ll be present – and in a condition to eat your fly.
A rough calculation follows (length in mm):
Therefore, the average daily loss in somatic weight of
males was 1.63 g at 359 mm, 9.37 g at 493 mm,
and 5.75 g for mean-sized males of 428 mm. For
females the average daily loss in somatic weight
was 5.75 g at 421 mm, 18.87 g at 531 mm, and
12.47 g for mean-sized females of 477 mm.
Daily weight loss can be used to suggest how
long fish of different sizes can remain in freshwater
before death. The amount of weight loss which
results in death of shad is not known, but death
occurs in many animals when weight loss exceeds
40% (Curtis 1949).
If death occurs at 40% weight loss and it becomes morose and lethargic at about 30%, then a 359mm male (14”) that weighs about a pound, will not be interested in flies in about 82 days. Females lose weight even faster, so if you’re looking for the biggest fish you’ll need to fish almost as soon as they arrive.
… and you thought Science was for eggheads.
Shad feed in fresh water, but as plankton is less available they’ll opportunistically feed on aquatic insects, baitfish, shad eggs, and terrestrials.
Stomachs of fish collected upstream
from Port Jervis, N.Y. (295) in late May and June
frequently contained a few insects. I observed a
large mayfly hatch in late May 1964 near Hancock:
hundreds of adult shad were rising to the
surface, apparently to feed, and the stomachs of
many fish (about 50) captured by angling were
packed with mayflies. Similar surface feeding behavior
was observed on several other occasions,
although fish were not collected to confirm feeding.
Many adults captured during the Tri-State
Surveys contained recently eaten young shad and
shield darters, Percina peltata.
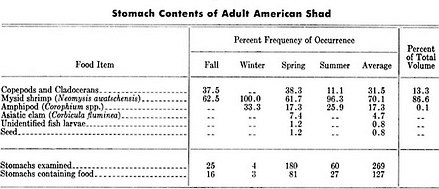
The California Fish & Game department has confirmed Shad feeding in the Sacramento delta, and the results of their trawls of the Sacramento River and Delta are shown above.

Which suggests there may be a couple of dozen other flies we haven’t considered – and the above lends a little credence to the red/white shad darts that have been effective for decades. Feeding habits are ruled by opportunistic prey and local conditions, and much science cites the link between small shad and terrestrial insects, and in many cases their stomach contents were disproportionately (greater than 20%) comprised of terrestrials.
Most migratory movement within a river system occurs between 9AM and 2PM, with numerous studies describing increased activity during daylight hours – and spawning commencing with dusk:
Females release their eggs close to the water surface to be fertilized by one or several males. Diel patterns of egg release depend upon water turbidity and light intensity. In clear open water, eggs are released and fertilized after sunset (Leim 1924; Whitney 1961), with peak spawning around midnight (Massmann 1952; Miller et al. 1971; 1975). In turbid waters (or on overcast days; Miller et al. 1982), eggs are released and fertilized during the day.
As my beloved American River is choked with spawning Striped Bass at nearly the same time, it’s important to note the tender regard for Shad held by the larger predatory bass:
A recent study strongly supports the hypothesis that striped bass predation on adult American shad in the Connecticut
River has resulted in a dramatic and unexpected decline in American shad abundance since 1992 (Savoy and Crecco 2004). Researchers further suggest that striped bass prey primarily on spawning adults because their predator avoidance capability may be compromised at that time, due to a strong drive to spawn during upstream migration.
– via American Shad, Chapter 2
 American Shad also hold an esteemed standing in American history, largely because of their role in feeding Washington’s army at Valley Forge. Alosa sapidissima is translated as “Very Delicious” and a starving patriot could ignore all those small bones as it chewed better than frozen boot sole …
American Shad also hold an esteemed standing in American history, largely because of their role in feeding Washington’s army at Valley Forge. Alosa sapidissima is translated as “Very Delicious” and a starving patriot could ignore all those small bones as it chewed better than frozen boot sole …
The 2010 version has a few percentage points in Nitrosamines and PCB’s but the gastronomic benefits speak for themselves. Oily fat calories capable of sustaining a nation on the verge of independence.
Fast food has since become the 51st star on Old Glory, and it’s Pizza Hut that nourishes most of Afghanistan and Iraq.
For the rest of us gourmands it’s the Indian legend that holds more weight than precious Omega-3 fatty acids:
Shad are richly flavored thanks to a good bit of omega-3 laden fat, but they are among the boniest fish in the world. An old Indian saying has it that a porcupine fled into the water and was turned inside out to become the shad. It is not far off.
Tags: American Shad, Tsung Tzu, Alosa Sapidissima, shad feeding in freshwater, American River, Omega-3 fatty acid, Mycid shrimp, fly fishing for shad, fly fishing blog

I think The Founding Fish by John McPhee a fine read.
Pingback: Tweets that mention Singlebarbed's (oddly) special insight into the West Coast run of the American Shad (why they're bigger earlier) -- Topsy.com
I have always been told that when the shad are in the American river they are not eating, and them hitting flies or lures was an instinct thing.
That’s what I was told as well – it appears that is wrong. Shad will feed on anything available but the huge schools likely make the pickings extremely slim.
The links posted above will take you to the documents and research, all agree that Shad feed in freshwater – but food is rarely available in enough quantities to sustain their weight (they’re moving upriver and expending lots of calories in the process).
Pingback: In Spring a young man’s thoughts turn to Invasives? | Singlebarbed
Pingback: In Spring an Old Guy’s thoughts turn to divorce, or the encroaching Bony Silver Menace | Singlebarbed